TOTAL SECURITY SOLUTION
SOLUTION
Competitive Edge of KJ TECH Face Reader
01
Enhanced Recognition
Speed and Accuracy
Powered by deep learning Al algorithms and achieving recognition speeds of 0.3-1 second with over 99.99% accuracy and significantly reduced False Acceptance Rate in diverse environments such as twin detection and different skin colors.
02
Environmental Stability
Equipped with infrared (IR) and 3D depth sensors ensures robust authentication performance regardless of ambient lighting
conditions or user appearance changes such as glasses, masks, hats etc.
03
Enhanced Security Features
Protected by advanced security features including 3D depth mapping, IR sensors, and liveness detection to prevent spoofing
attempts using photos, videos, or 3D models.
04
Improved User Experience
Featured with wide-angle lenses and Al-
based tracking for recognition during natural
movement and user-friendly display design for
intuitive authentication experience.
05
Advanced Data Processing and Privacy Protection
Protect privacy by storing only encrypted
biometric templates, not facial images
(compliant with international data protection
regulations including GDPR).
06
Multimodal
Authentication Support
Supports multiple authentication methods including
facial recognition, fingerprint, palm vein, QR code,
NFC/Bluetooth, PIN, and card authentication for
enhanced flexibility.
07
Installation and Maintenance
Supports easy installation with remote software upgrades and maintenance capabilities and self learning Al improves performance over time.
08
Cost Efficiency
Provides more affordable high-performance
solutions due to technological advances and
reduced operating costs through improved
energy efficiency.
09
Customization and Scalability
Supports expandable software and hardware
capabilities with OEM/ODM support for tailored
solutions meeting partner requirements.
Biometrics
Biometrics refers to the information used as one of the authentication procedures by informatizing a part of a person’s body that can be identified from others.
These individual characteristics can be used as a security solution in many ways and have the following advantages.
Biometrics refers to the information used as one of the authentication procedures by informatizing a
part of a person’s body that can be identified
from others. These individual characteristics can
be used as a security solution in many ways and
have the following advantages.
01
There is no fear of loss.
02
There is very little concern about copying and stealing.
03
There is no need to carry separate items.
In other words, it has the characteristics of uniqueness, accuracy, convenience, economy, and universality.
Fingerprint
Human fingerprints consist of various types of options.
These fingerprints are classified based on decades of Henry System.
Henry System is a method of distinguishing features through classification criteria such as left loop (fingerprint with a line shape to the left), right loop, rch (semi-circular pattern), whorl, and tented arch (semi-circular curve like a tent).
Among the features of fingerprints, two-thirds are annular lines, one-third are swirls, and about 5%-10% are arched.
However, this classification is used only when a large amount of crime DB is used, but is not well used in fingerprint recognition (biometrics) technology.
Instead, in fingerprint recognition (biometric recognition), lines that interfere with the smooth flow of ridges become the basis data for most fingerprint recognition authentication.
According to a record of the features of fingerprints introduced by Galton in late 1800, most of them are at the point where the ridges are divided into two, the ridges at the beginning and end of the ridges. There are various minuteiae (characteristic point), which is dots (a very small melting point (a melting point seen as a point), islands (a melting point a little longer than the melting point), but a melting line (a melting line such as an isolated point), a pods or a split space (two spaces).
Human fingerprints consist of various types of options. These fingerprints are classified based on decades of Henry System. Henry System is a
method of distinguishing features through
classification criteria such as left loop
(fingerprint with a line shape to the left), right loop,
rch (semi-circular pattern), whorl, and tented arch
(semi-circular curve like a tent).
Among the features of fingerprints, two-thirds are
annular lines, one-third are swirls, and about
5%-10% are arched.
However, this classification is used only when a
large amount of crime DB is used, but is not well
used in fingerprint recognition (biometrics) technology. Instead, in fingerprint recognition
(biometric recognition), lines that interfere with the
smooth flow of ridges become the basis data for most fingerprint recognition authentication.
According to a record of the features of fingerprints introduced by Galton in late 1800, most of them are at the point where the ridges are divided into two, the ridges at the beginning and end of the ridges. There are various minuteiae (characteristic point), which is dots (a very small melting point (a melting point seen as a point), islands (a melting point a little longer than the melting point), but a melting line (a melting line such as an isolated point), a pods or a split space (two spaces).
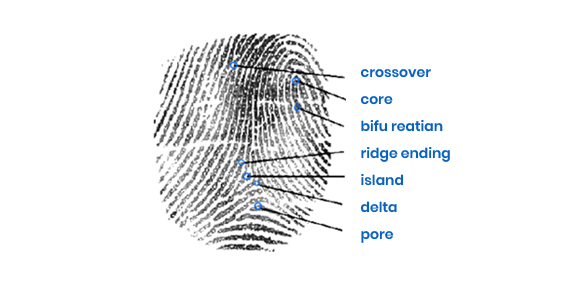
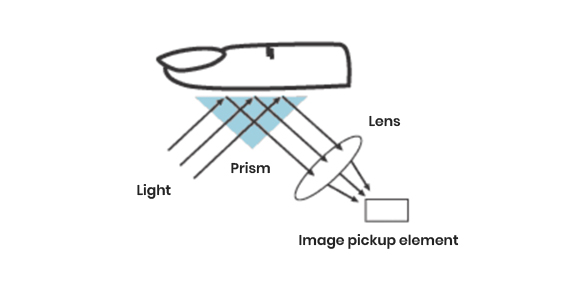
Other features, such as fingerprint recognition, are very important elements, such as the core,
which is mainly the inner axis at the center of drawing vortexes, rings, or arches, and are mostly made at the ends of several curved ridges and ridges.
Delta is generally located at the bottom left or right of the fingerprint at the continuous end of a triangular ridge.
The ridges have fine sweatholes at a certain distance, and the initial attempts at fingerprint recognition used the location and
distribution of these sweatholes as data for authentication.
The resolution required to capture these sweatholes continues to increase.
Other features, such as fingerprint recognition, are
very important elements, such as the core,
which is mainly the inner axis at the center of
drawing vortexes, rings, or arches, and are mostly
made at the ends of several curved ridges and
ridges. Delta is generally located at the bottom left
or right of the fingerprint at the continuous end of a
triangular ridge. The ridges have fine sweatholes
at a certain distance, and the initial attempts at
fingerprint recognition used the location and
distribution of these sweatholes as data for
authentication. The resolution required to capture
these sweatholes continues to increase.



